S> Pt. c/o soreness with compression however denies any other dizziness, numbness, weakness, pain on the lower leg, or SOB.
O>
VS: T 36.8 C BP 104/63 HR 74 RR 18 SpO2 95% Pain 5 Ht 172.0 cm(68") Wt 103.1 kg BMI 34.8 BSA 2.22 (09/02 11:16-09/03 03:00)
Focussed exam:
Rt. Groin hematoma: size around 10cm. firm -> soft after compression.
No bruit nor thrill.
Mild tenderness
Strong palpable peripheral pulses
Warm lower leg
AP>
# Iatrogenic groin hematoma:
- hemodynamically stable, no tachycardia
- arterial access
- manual compression for 20minutes -> stop expanding
- frequently check site, peripheral pulses
- stat CBC, type and screen
- doppler to evaluate hematoma/hemorrhage/AVF
- if hgb drops or turns hemodynamically unstable, then resuscitation(fluid, blood transfusion) and vascular surgery consult with CTA
WHAT - HOW - WHY
when,where,who = no needed....
# Pacemaker placement or upgrade related bleeding.
- likely procedure related bleeding vs. hematoma
- VSS
- f/u H&H, type and screen sent
- CXR
- USG: chest soft tissue evaluation; however if Hgb drops or becomes hemodynamically unstable, then consider immediate CTA.
- conservative management for now.
- EP evaluation in AM
# PNA
-CAP
-HCAP
-HAP
(Definition)
-How to Diagnose PNA (Sx/Lab and Image)
- ID consult
- Further workup such as labs, bronchoscopy
- Fungal culture
- LDH for PCP
- Mycoplasma
- Mycobacteria(concerning like weight loss, night sweating, more than 2weeks)
=> airborne precaution, AFB.
- Legionella Urinary Ag
-How to manage it per setting
CAP
HCAP
HAP
Immunocompromised
(symptom = mild mild mild but CT shows something)
- ceftriaxone(1g IV Q12HR) + levaquin(750mg IV qday) for 7 days...
# Urinary Tract infection(UTI)
The Diagnosis of Urinary Tract infection in Young children (DUTY): a diagnostic prospective observational study to derive and validate a clinical algorithm for the diagnosis of urinary tract infection in children presenting to primary care with an acute illness.)\
UA:
we compared the number of squamous epithelial cells (using 10 or more squamous epithelial cells as a cut-point) in contaminated and uncontaminated samples
(REF:
Sx: Lower UTI
Upper UTI
AMS(without any other specific reason)
Tx. Oral= Cefdinir 300mg BID po 5-7days.
# Aortic ulcer
# Toothache: Periodontitis
- treat with antibiotics?
- treat with swish and swallow
Meds
1) 0.12% oral chlorhexidine treatment q12hr and(swish and spit out)
2) Antibiotics: Augmentin X 14 days.
Acute simple gingivitis rarely requires systemic antimicrobial therapy. Chlorhexidine 0.12% oral rinse can be used in most cases. Antibiotics are usually indicated for patients with rapidly advancing disease, severe pain, or an immunocompromising condition. Possible regimens include penicillin plus metronidazole, amoxicillin-clavulanate, or clindamycin (table 2).
3) Severe disease (Parentral treatment)
# Smoker:
Chantiks??
Transdermal patch: Topical: Note: Adjustment may be required during initial treatment (move to higher dose if experiencing withdrawal symptoms; lower dose if side effects are experienced).
Patients smoking >10 cigarettes/day: Begin with step 1 (21 mg/day) for 6 weeks, followed by step 2 (14 mg/day) for 2 weeks; finish with step 3 (7 mg/day) for 2 weeks
Patients smoking ≤10 cigarettes/day: Begin with step 2 (14 mg/day) for 6 weeks, followed by step 3 (7 mg/day) for 2 weeks
#
bedbugs: contact precaution, epidemiology contacted.
- skin care: topical hydrocortisone and/or
oral antihistamine
- clean belongings
- education: call experienced pest management
and wash/dry with hot temp (at least 50C)
# Lice:
- contact precaution, epidemiology
- topical permethrin or oral ivermectin (for classic scabies)
- topical permethrin and oral ivermectin (for crusted scabies = old or immunocompromised)
for 1-4 weeks.
if after 4weeks, then consider to change meds or check adherence.
- Skin care(for nodule): topical hydrocortisone
# Tick Bite
-Tick found in clothing and on patient's left arm pit
-Removed by RN - no residual tick remanents left, area cleaned with alcohol
-Tick is possibly a male lone star vs deer tick
-Spoke with ID - treat prophylactically with Doxycycline 200mg PO once
-Monitor area for rash, warmth, swelling, and fevers
# Acute PE:
(Stable PE)
- heparin infusion
- workup for DVT
(Unstable PE)
- VS= unstable, indicated for tPA.
(Ix.)
(CTx.)
-
Stop heparin infusion
- Start tPA(20mg IV bolus and 80mg infusion for the next 2 hours or just infuse
100mg for 2 hours)
(If there is bleeding on tPA)
- STOP STOP STOP
- cryoprecipitate 10 units + FFP 2 units
- protamine sulfate 1mg : 100 units of heparin(if 2 hours later, then 0.5mg : 100 units; half dose)
# LHC radial hematoma:
- Oozing: re introduce TR band with protocol
- Hematoma: Manual compression(20 mins)
- 15mins/30mins/1hour/2hours monitor
-
2 hours from hemostasis: resume heparin.
(cf. general ablation or other cath protocol: 4 hours after hemostasis! with half dose of AC!)
- no ice pack
- manual compression and conservative management
# Hypertensive emergency:
- end organ damage
- AKI, Encephalopathy, Vascular emergency(ACS, Stroke), and ADHF(pulmonary edema)
- Goal: reduction 10-20% in 1 hour and rest of part during 23hours.(goal -25% in a day)
- After 24hours: normalize to
<130/90 (?)
[setting]
- HF:
- Avoid BB, CCB and nor hydralazine
- Mainly IV NTG !!! (+- Other vasodilator and Enalaprilat) or NTG patch
- Aortic dissection:
- ACS
- Encephalopathy
[medication onset - peak - duration]
Labetalol IV: onset quick - peak 3 hours - duration for 12 hours.
# PM placement with compliacted Pneumothorax f/u:
Left sided pneumothorax
-s/p chest tube placement on 4/29
-repeat xray 4/30 with enlarging pneumo and chest tube retraction by 2 inches (may have occurred when patient went for xray);
-CXR with worsening pneumothorax on connecting the chest tube to water seal - now back to suction.
Tachy/brady syndrome s/p MDT VVI PM
-s/p Medtronic VVI PM implant; difficult procedure due to Left axillary venous access
-Device interrogation looks good
-Device site looks good
-continue chlorhexidine and mupirocin through 5/2
-Remove waterproof Aquacel dressing after 1 week.
-Avoid lifting left arm above the shoulder or lifting weight for 4 weeks.
-Follow up Dr. Koneru 6/5/20 CMH
# Renal patient with hyperglycemia
CrCl 10 to 50 mL/minute: Administer 75% of normal dose and monitor glucose closely.
CRRT: Administer 75% of normal dose and monitor glucose closely; supplemental dose is not necessary
CrCl <10 mL/minute: Administer 50% of normal dose and monitor glucose closely.
HD= consider as CrCl<10mL: 50% of normal dose. Especially long acting should be lowered or initial dose should be lowered. Transitioning with lower dose => keep goal 180-200. Hard to manage but this is it!
# Central line removal form:
Pt. is hemodynamically stable but indicated to central line removal with highly suspicious of CRBSI. I explained patient regarding possible risks of procedure including air embolism, bleeding, hematoma, catheter fracture, dislodge of thrombus and benefit of controlling the source of infection. He agreed to get procedure done. Pt. was asymptomatic currently and stable VS. Neck was evaluated and positioned him to Trendelenburg position with educating him of Valsalva maneuver. Removed dressing and suture. After removal of old dressing, sterilized area with chlorhexidine and pulled central line with pt.'s Valsalva maneuver. Applied pressure on the site of IV insertion for 10 minutes and will keep him in the supine position for 30 minutes. No bleeding, hematoma, nor any distress currently.
Suspicious of CRBSI:
- Leukocytosis(>14K), fever(101F) but no altered mental status, stable VS but tachycardia related to cardiac transplant status.
- Central line placed about 2 weeks ago.
- Mild local sign of infection(redness but no discharge) without other source of infection identified.
- d/t given risk of immunosuppression with central line => highly suspicious of CRBSI
- empirical antibiotics started
- central line removed.
- close monitor site, VS, and tip culture sent.
Tae shik Park, MD
Cardiology Hospitalist
p3490
# CRBSI: (IDSA ? recommendation?)
- no other source of infection but definitely infected ?
then suspect CRBSI
- remove CATHETER ! with sepsis for sure.(or immunosuppressed! but VAD patient? = not right away
)
1) significant => remove it asap
2) not significant but evidence of infection without other source => remove it
3) not significant with other source => leave it !
-
# OHT rejection treatmnet:
Acute antibody mediated cardiac allograft rejection.
Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita.
Status post orthotopic heart transplant.
Chronic immunosuppression.
Start on home dose of mycophenolate mofetil (1500 mg twice daily) and prednisone (5 mg twice daily).
Old tacrolimus. Check tacrolimus trough level in the morning.
Will give 1 dose of IV methylprednisone 1000 mg. Will consider given 2 more doses.
Continue with home dose of aspirin and losartan.
Continue with home dose of atorvastatin.
Start on home dose of dapsone, nystatin and valganciclovir.
Will get HLA class 1, HLA class 2 and (angiotensin type 1 receptor antibodies; only for antibody mediated rejection)
# Acute OHT rejection:(tx. per cellular vs Ab mediated and/or grade!)
- RHC(10/1/2020) showed acute cellular rejection(ISHLT grade 1R), acute antibody mediated rejection(pAMR2)
- VSS, Mild symptom of HF(orthopnea)
- Basic labs: CBC, CMP, PT/PTT, Troponin, BNP, Lactate
- OHT labs: Tacrolimus Tr
- TTE, Repeat RHC in 2 weeks or earlier
- Solumedrol 1g IV X3 and/or ATG(Anti-thymoglobulin therapy)
- Consider to repeat plasmapheresis, IVIG ?
- Continue MMF 1500mg Q12hr, Tacrolimus(4/4 mg)
# OHT with possible stroke, supratherapeutic INR.
IVF: 250cc bolus and f/u with 75cc/hr of NS
Assessment:
- dehydration
- hypovolemic hyponatremia
- diarrhea
- acute renal failure, likely multifactorial (dehydration, Bactrim)
- s/p LVAD
- chronic anticoagulation with coagulopathy, status post vitamin K 5 mg p.o. 04/30/2020
- elevated LDH, no evidence of pump thrombosis on log file analysis
Rule out outflow obstruction, although pump interrogation is unremarkable
Inflow appears patent on echo
Rule out non hemolysis source of LDH elevation
- slurred speech, possible TIA, symptoms resolved
- chronic polymicrobial driveline infection - currently no symptoms
- DL infection: send blood culture + DL drainage culture for sure !!
Plan:
- COVID-19 screen negative
- stool for C diff
- chest x-ray
- blood cultures, wound cultures, urine cultures
- empiric coverage with vancomycin and Zosyn
- holding warfarin for now, restart if no surgical intervention needed
- start bivalirudin drip when INR < 3.0, PTT goal 80-100
- aspirin 81 mg daily when INR < 3
- LDL isoenzymes ordered
- hold hydralazine
- I independently reviewed echo images from today; my interpretation: Small LV chamber size consistent with hypovolemia, no thrombus on inflow cannula, low diastolic flows, aortic valve persistently closed, RV cannot be well assessed, but does not appear severely dilated, although dysfunctional
- IV hydration with normal saline
- nephrology consult
- No LVAD speed change today.
- the rest is per the APP's note.
# OHT infection(respiratory) + rejection !!:
affect, cooperative
ASSESSMENT:
Status post heart transplantation, clincal rejection with new high MFI DSAs and systolic dysfunction by echo, concern for AMR
Chronic immunosuppression.
Abnormal CT Chest
Hypertension, controlled on Losartan
PLAN:
1. Start Solumedrol 1gm daily X 3 days. Resent HLAs and HLA AT1R
2. Continue Cellcept 1500mg BID and increase Prograf to 7mg BID. He admits to taking his Prograf late before his clinic draw Monday morning. He took 6mg late Sunday night before clinic monday morning last week.
3. Start prophylaxis as I anticipate he will be getting long steroid taper with treatment for AMR
4. Continue
Vanc and Zosyn for abnormal CT Chest. Blood cultures sent and CMV PCR, Fungitell and Platelia sent as well. Will consult transplant ID for further recommendations.
5. Continue ASA, statin - if he gets hypotensive again then we may need to drop his Losartan or hold altogether
6. Plan for RHC/EMBx on Monday. NPO after midnight.
7. Transfer to ICU for steroids today and careful monitoring.
===> Discharge plan:
1. Discharge: home today after plasmapheresis and IVIG completed
2. AMR Management:
-Final session of plasmapheresis and IVIG today (4/29)
-Repeat HLAs and AT1R drawn this AM (4/29) remain pending
-Will undergo following OP treatment plan: 4 doses of Velcade and 2 doses Eculizumab
-OP treatment will begin on 5/1/2020
-Continue Losartan 25 mg once daily for AT1R antibodies
3. Immunosuppression:
-Continue Envarsus at 10mg PO qd
-Continue trending daily tac levels, tac 11.4 this AM (4/28)
-Continue MMF 1500mg PO BID
-Continue Prednisone 5mg PO BID
4. Immunoprophylaxis
-Continue Dapsone 100mg PO qd - will need 6 month course
-Continue Nystatin 5mL swish and swallow
-Continue Valcyte 900mg PO bedtime - will need 3 month course
-Continue Penicillin V potassium 500mg PO bid
5. CAV Prophylaxis:
-Continue ASA 81mg PO qd
-Continue Lipitor 10mg PO qd
6. Electrolyte Management:
-Continue Mag oxide 800mg PO qd
-Encourage low-potassium diet given recent hyperkalemia
-K 4.7 this AM (4/29)
7. PSY Management:
-Psych and addiction medicine consults completed
-Pt confirms he would like to follow-up with psychiatry as OP
-Provided pt with OP PSY contact info as he is deciding between establishing therapy closer to home vs. VCU
8. Discharge Logistics and Follow-Up Items:
-Pt drove himself to the hospital and will transport himself home- he is at his baseline mobility and on no sedating meds
-Will return to OP clinic on Friday (5/1) for Velcade and Eculizumab at 8AM on Gateway 7
-On 5/1, pt will be receiving Velcade dose 2 of 4 and Eculizumab dose 1 of 2
-Pt will receive Velcade weekly until completing his 4th dose and will receive his Eculizumab doses two weeks apart
-Repeat Tac level, BMP, Mag, CBC and Hepatic panel orders placed for Friday 5/1/2020
-CC confirmed HH set up to monitor trialysis line (Personal Touch Home Health Agency)
-Remaining Vaccination Schedule: Meningoccocal Conjugate (Menveo) 6/25/2020, Meningococcal Group B 5/25/2020
# Acute Diarrhea: in light of OHT status.
- less likely thyroid disease, food poisoning but likely infectious? d/t immunocompromised status
or colchicine related.
- unlikely pancreatitis or hepatobiliary disease
- Labs: TSH; Infection workup: Stool study(C. diff, WBC, RBC, Stool pathogen and parasite workup including Cyclospora, Giardia, Cryptospordium) d/t cat bite and risk of zoonosis.
;Transplant patient: CMV, EBV and IVIG level
- no antibiotics indicated at this point however Ceftriaxone started for the other indication as above
- contact plus precaution
- IVF for now
# Acute Rejection in cardiac transplant(less than 1 year):
46yo male s/p OHT (10/2019) presenting with shortness of breath, volume overload, potential rejection.
1. OHT, Possible cardiac allograft rejection
-significant
decrease in BiV systolic function(
Bedside ECHO - really important!)
Plan
1. For possible rejection:
-RHC w/biopsy in the AM
-
Start methylprednisolone 1 g x 3 doses (4/29-5/1)
-
HLA labs: class I, class II, and AT1R ordered 4/29
2.
Start Dobutamine 3 mcg/kg/min
3.
Continue Lasix 40 mg daily - may increase to bid if inadequate urine output
4. Hold Apixaban for procedure; start
Heparin gtt(rejection related thrombosis?)
5. Continue immunosuppression:
-Tacrolimus 3 mg in AM, 2 mg in PM; will check level with AM labs
-MMF 1500 mg bid
-Hold Prednisone until 5/2(d.t solumedrol)
6. Continue immunoprophylaxis, CAV prophylaxis
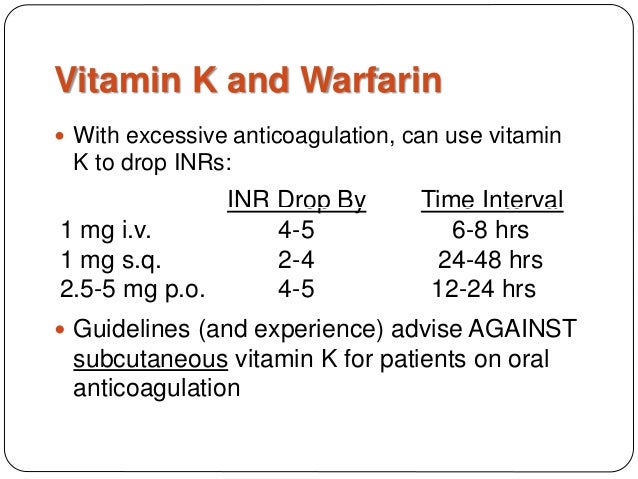
# Warfarin reversal
- INR >1.5 s/p Vitamin K 2.5mg
- Vital, H&H and INR(after 12 hours. )
Onset of action: Increased coagulation factors: Oral: 6 to 10 hours; IV: 1 to 2 hours
(f/u 12 hours vs. 6 hours, respectively. Warfarin has nearly 100 percent oral bioavailability = oral = IV dosing.)
Peak effect: INR values return to normal: Oral: 24 hours; IV: 12 hours
# Warfarin reversal with supratherapeutic INR and BLEEDING.
- Severity(Evaluation and Management): what, how
- check symptom
- vital sign: tachycardia and hypotension(significant! emergency situation = ICU)
- labs: PT/INR, PTT, CBC stat.
= assessment.
- IVF(1L), labs: CBC, Hgb stat, BMP stat(for possible other cause or organ damage)
- type and screen for emergent blood transfusion.
= emergent management.
- Cause(Warfarin -> Reversal; investigate where it is?!!?): why
- reversal of INR= IV 10mg phytonadione.INR Q6HR (or IV 5 - 10mg per severity or INR)
-
FFP 2units vs. 4 units
or 4F PCC 2000 units and/or additional INR q15mins.
- Image workup: CTA basic(if kidney function problem => IR or GI or Uro. contact) or
USG/dry CT(initial can be this one).
; Vitamin K 10mg IV(for 1 hour, after 24hours, if it's still high, then give next dose!)
;
FFP(10-15cc/kg IV; recheck INR q2HR and repeat as needed. =>
in general 2 units for moderate
or 4 units for severe at once. )
or 4F PCC(KCENTRA; TOC;
We suggest a 4-factor prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC; INR 2-4; 25units/kg, 4-6; 35units, >6; 50units. OR 2000units + 50units*n)
(table 2) rather than a 3-factor PCC and/or Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP))
or 3F PCC.
***
(NO BLEEDING and INR 5-8.9 =
2.5mg phytonadione oral; 9.0 = 2.5 or 5mg phytonadione oral or IV 1-2.5mg by slow. Recheck INR Q12hours and repeat if it's necessary )
Guideline recommendations for management of warfarin-associated bleeding and/or high INR
| Clinical setting | 2018 ASH guideline | 2012 ACCP guideline |
- Serious or life-threatening bleeding
- Any INR
|
- 4-factor PCC
- Vitamin K (intravenous)
- Hold warfarin
|
- 4-factor PCC*
- Vitamin K (intravenous)
- Hold warfarin
|
|
| (No recommendations given) |
- Vitamin K (oral)
- Hold warfarin
|
- No bleeding
- INR 4.5 to 10
|
- Hold warfarin
- No vitamin K
|
- Hold warfarin
- Vitamin K (low dose, oral) is optional
|
| A. If 4-factor prothrombin complex concentrate (4F PCC) is available (preferred approach): |
| 1. Give 4F PCC(2,7,9,10 and C&S) * 2000 units¶ IV over 10 minutes. Check INR 15 minutes after completion of the infusion. If INR is not ≤1.5, give additional 4F PCC (500 units repeatedly!!! refer to topic or drug reference for details). |
| 2. Give vitamin K 10 mg IV over 10 to 20 minutes. |
| B. If 3-factor prothrombin complex concentrate (3F PCC) is available but 4F PCC is not available: |
| 1. Give 3F PCC(2, 9, 10 without 7)* 2000 units¶ IV over 10 minutes. Check INR 15 minutes after completion of the infusion. If INR is not ≤1.5, give additional 3F PCC (refer to topic or drug reference for details). |
| 2. Give Factor VIIa 20 mcg/kg IV OR give FFP 2 units IV by rapid infusion. Factor VIIa may be preferred if volume overload is a concern. |
| 3. Give vitamin K 10 mg IV over 10 to 20 minutes. |
| C. If neither 3F PCC nor 4F PCC is available: |
| 1. Give FFP(all factors, fibrinogen, C&S, everything) 2 units IV by rapid infusion. Check INR 15 minutes after completion of infusion. If INR ≥1.5, administer 2 additional units of FFP IV rapid infusion. Repeat process until INR ≤1.5. May wish to administer loop diuretic between FFP infusions if volume overload is a concern. |
| 2. Give vitamin K 10 mg IV over 10 to 20 minutes. |
cf) in DOAC with bleeding = can be treated with 4F PCC(2000 unit once!)
# Warfarin maintenance adjustment protocol(conservative method - avoid unnecessary bleeding)
Warfarin PK:
Onset of action: Initial effect on INR 24-72hours. BUT Full therapeutic effect generally seen between 5 and 7 days. Prothrombin (factor II), which has a half-life of 72 hours.(no addtional synthesis however stay longer!!! than Protein C&S which has short half-life = disappeared really quick(anti-coagulant; 8hours), it can paradoxically increase the coagulation tendency leading to massive thrombosis with skin necrosis and gangrene of limbs.
1) initiation: 5mg and 72hours rule!(1.5=increase, 1.9 continue, 2 decrease, 2.5 hold)
5mg -> check INR in 2-3days(48-72hours rule; supratherapeutic needs to be checked in 1-2days)
<1.5 = 7.5mg daily
<1.9 = 5mg daily
2 = 2.5mg daily
>2.5 = hold and recheck in a next day. -> recheck in next day.
-> generally recheck in 2-3days after adjustment.(for adjusting protocol 72hours.)
<1.5 = 10mg
<1.9 = 7.5mg
2 = 5mg
>3 = hold and recheck in a next day.(supratherapeutic - will test in a day exceptional)
** Oxford protocol
5mg for 3 days
<1.5 = 10mg
1.5-2 = 5mg
2-2.5 = 3mg
2.5-3 = 1mg
>3 = hold
recheck in a day(day #4)
<1.5 = 10mg
1.5-2 =5-7.5
2-2.5 =5mg
2.5-3=3mg
3-3.5 =2mg
>4 = 0mg
recheck in a day(day #5..)
2) f/u (after initiation)
every 2-3days until INR within therapeutic range on 2 consecutive INR
(2 times = 3days X2 = almost a week.)
Then every week until within therapeutic range on 2 consecutive INR
(2 times = 1weeks X2 = almost 2 weeks)
Then two weeks until...
(2 times...)
Then four weeks until
Then monthly. (generally 1 month => if it's stable for 6 months then 2 months maximum)
3) maintenance f/u and frequency
Change in diet, medication such as transient effect.
-> recheck in 3-5 days.(72hours rule!)
# Adjustment by 5-10% (regularly 5-10% in a week dosage change =
5% = 0.5 change in INR (if INR <1.9 = 5%)
10% = 1 change in INR (if INR <1.6 = 10%)
20% = 2 change in INR (if INR <1.2 = 20%)
booster dose can be given 1.5 times higher dose once!(if it's subtheerapeutic)
hold 1 dose can be done once if it's <4.5(if it's supratherapeutic)
-> recheck in 1-2weeks.
* exceptional range(considered to be transient !!!)
INR > 4.5 - 10 without bleeding = hold 2 doses and/or Vit K(oral 1mg) can be given.
recheck in 3-5days
INR >10 without bleeding = hold 2 doses and Vit K(oral 2.5mg) can be given and
recheck INR daily until it's therapeutic. Then resumed at a lower dose(20% for sure).
TIPS>
If INR <0.5 range out of target and previously stable = continue and recheck in 1-2weeks.
Otherwise need to adjust with omitting/boosting and adjustment.
Interaction
a) Amiodarone: day 7 of amio = decrease 25% weekly dose
day 14 of amio = decrease another 25% weekly dose
(target: 50% reduction in weekly warfarin dose
after 2weeks of interaction)
-> check INR after
7days, 14days and 21days. = weekly
like maintenance adjustment
b) fluconazole, metronidazole, bactrim = day 1 of interaction = decreased 30% weekly dose
-> check
INR "3"-5 days (transient one rule)
c) all other interaction -> check
INR "3"-5 days and adjust as indicated.
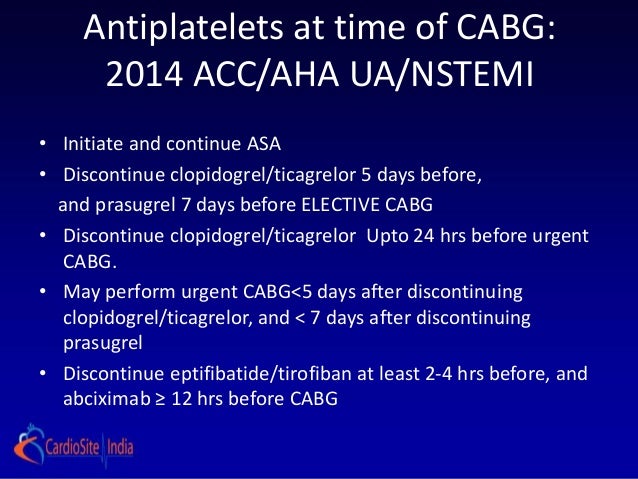
# Periprocedural AC(on holding vs. Bridging):
- DVT s/p IVC, on DOAC
- referred for RHC and Biopsy as part of his OHT surveillance
-> Hold 2 days of
Apixaban(3 doses) prior to RHC with EMB
- LHC# Atypical CP:
likely 2/2 SVT and/or NSTEMI (likely type II but abnormal EKG might reflect underlying disease)
less likely aortic dissection, PE, GI
- Aortic Dissection Detection Risk score(ADD-RS): 1, will get d-dimer
- BP both arms.
- Wells score for PE: 0
- serial troponin and EKG
- trending down troponin
- if d-dimer is elevated >500ng/mL, then will get CTA asap.
- basic labs: CBC, CMP, PT/PTT, troponin, BNP
- CXR, TTE
- Consider CTA if it's indicated.
- ASA, Ticagrelor loading, heparin infusion, atorvastatin were initiated.
- d/t bradycardia, b-blocker was held.
# SVT:
- likely autonomic drive?
- s/p adenosine 6mg, 12mg
- currently NSR
- likely 2/2 ischemic drive.
# Aortic dissection
: Typical history = ?
Mr. Morris is a 47 y/o M with PMH of HTN, HFpEF (EF 70%), OSA (wears CPAP at night), CVA in 2016 (no residuals), and CKD Stage IV who presented to the ED on 4/15/2020 with complaints of chest pain. Per the patient he was moving heavy furniture prior to arrival when he had acute onset of chest pain, states it has been happening intermittently over the past few months but was significantly worse this time. He endorsed SOB but denied diaphoresis, n/v, or palpitations. EKG showed acute MI with depression in Leads 2 and 3 and elevation in V2, given ASA in EMS. He endorses that he has missed several doses of his medications because he forgets to take them.
He was initially admitted to the stepdown unit for ACS work-up. Cardiac enzymes were negative overnight. ECHO completed 4/16 was concerning for dissection, CTA completed which revealed Type A dissection which extends to the left common iliac artery. CT Surgery was consulted and he was posted SN 2 for the OR. He was brought to CSICU for blood pressure management and monitoring until OR.
vascular:
47 YO AAM with PMH HTN, OSA, HFpEF (55%), CVA in 2016 ( no residual deficits) and CKD IV (not on dialysis, producing urine) presented to the ED 04/15/2020 with chest pain. Pt with EKG findings of acute MI on admission and underwent echo that demonstrated possible dissection followed by confirmatory CTA. Vascular surgery consulted for Type A aortic dissection. Dissection extends to the left common iliac. Pt with no evidence of abdominal or lower extremity malperfusion.
No acute vascular intervention warranted, recommend CT surgery consult for repair of thoracic arch
Recommend admission to ICU for BP control systolic <120 HR < 70
Vascular will continue to follow
[CT surgery]
Surgical/Procedure Summary:
Plan for Type A
# Pregnancy and AHDF
# Pulmonary catheter
- way of placement and what to detect?
- indication?
- management?
# CDI: watery diarrhea >3/day.
[Classification]
- Risk(predisposition): abx. within 3 months(esp. Pc, Cef, LQ, and Clindamycin).
- Suspicion: elderly, elevated WBC, abdominal pain and fever
- initial encounter vs. recurrent
- nonsevere vs severe(WBC>15000 and/or Cr>1.5) vs fulminant(hypotension, toxic megacolon, ileus)
[Dx]
- labs: CBC, CMP, Stool(RBC, WBC, Cx. and C.Diff)
- images: (not routinely) unless concerning complication such as perforation, ileus, toxic megacolon. KUB -> CT
cf. Colonoscopy: for ileus, without diarrhea to see intracolonic inflammation(pseudomembrane)
[Tx]
- stop unnecessary inciting antibiotics.
- start to treat for 10 days of course
- non severe: oral vancomycin or fidaxomicin (same efficacy) >> metronidazole oral (lower)
- severe: oral vancomycin or fidaxomicin >> metronidazole
- fulminant: oral vancomycin + IV metronodazole.
- Recurrence(>more than 2 weeks from completion of therapy)
- if vanc was used => fidaxomicin or long term vanc(12weeks)
- if fidaxomicin or metronidazole => vanc for 10 days
- 2nd recurrence: as above or Vanc + followed by Rifaximin 400mg 3 times for 20days
or FMT.
# Anemia
- Reticount
- Iron testing
- Vitamin B12, Folate,
# IDA
- Iron saturation low
- Reeticulocyte count
IV iron regimen and F/U test
PO iron regimen and F/U test
DDx. Thalassemia
Normal; RBC count(5) X 3 = Hgb(15)
But Thalassemia; RBC count high but Hgb low (false positive anemia)
and Iron test
# Fever
- DDx. DVT/PE(d-dimer) or other Deep tissue inflammation such as pericarditis(hsCRP)
-
- Infection workup and empirical treatment
# HCAP vs CAP vs HAP
- definition
- CAP:
# COVID-19(PUI vs. Confirmed case):
- Risk factors
1) contact to COVID patient(within 14 days from sx. onset
; 14 days ago COVID - Sx. for now = still in risk; even general incubation in 3-5 days)
2) travel outside of country(within 14 days from sx. onset.) and (-) FLU
-----------------------------------------------------------------------> hx of exposure
3) SNF/LTAC; and (-) FLU and (-) RPP and no alternative Dx.
4) Old(>65) and chronic ds.(and/or immunosuppressed); and (-) FLU or (-) RPP and no alternative Dx.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------> community based weak population
- Lower respiratory symptom: SOB, Cough(and/or Fever) <-> cf. URI: rhinorrhea(nasal), sore throat
- mild vs. moderate/severe
- Basic labs: CBC, CMP, Troponin, BNP, TSH(in CHF labs)
- PUI labs:
- RPP(including FLU), COVID-19, sputum culture
- blood culture
- Images(CXR -> consider CT scan per severity)
- Ix. to send COVID 19 test with NPS(Risk, CXR, SOB, flu, RPP, no alternative dx. )
- mild resp. + risk factor; CXR(could be negative) = flu/RPP; send op. COVID-19 => home and self quarantine
- mod/severe resp.; CXR(b/l infiltration) = (-)flu OR (+) RPP but hypoxia(resting SOB);without alternative diagnosis;
call command center to guide.
- Precaution: Airborne precaution if there is Aerosol-Generating-Procedure such as CPAP/BIPAP, intubation, suction, high frequency oscillatory ventilation, tracheostomy, chest PT, nebulizer treatment, sputum induction, bronchoscopy.
(tube, bronco and even CPAP, Duobneb treatment)
*SOB/hypoxia -> regardless RISK(community possible enough) -> test negative and CXR infiltration -> Command center
*cough and RISK -> test negative and/or CXR infiltration -> still OP. COVID-19(Command center as needed)
*PPE regular: yellow(IP, hallway, and commute) < PPE contact(flu positive or PUI): new mask+gown
< PPE airborne(suction, intubation, etc.): N95 for sure. @ VCU.
# High flow oxygen (Liter, Rate) vs. High frequency oscillatory ventilation
# Endocarditis:
- Type: native valve/prosthetic valve
- Hx:
risk factors: history of IE/congenital/valvular heart disease
predisposing factors: IVDU, indwelling IV line, dental/surgical procedure, immunosuppression
- P/Ex:
vascular phenomana or immunologic phenomena:
septic pulmonary infarct, mycotic aneurysm, ICH, conjunctival hemorrhage, Janeway lesion(non-tender, small
erythematous/haemorrhagic macular, papular or nodular lesions on the palms or soles);
GN, Osler nodes(painful, red, raised lesions found on the hands and feet), Roth spots(hemorrhage in the retina with a white
center), RF * Janeway(non tender red) vs. Osler(tender raised red)
- NEURO(EYE), DENTAL, PALM AND SOLES.
- basic workup: CBC, CMP, PT/PTT, Troponin, BNP
- other endocarditis labs: Blood cultures X3, Rheumatoid factor, UA.(minor criteria)
ESR, CRP,
C3, C4, CH50 in subacute endocarditis. => not necessary though.
(hyperglobulin, cryoglobulin, IgG, hypocomplementemia, false positive syphilis test) =>(not necessary)
- CXR, TTE(consider TEE)
- EKG: evaluation for conducting system
- DUKE Criteria: 2 maj or 5 min (or 1+3)
- No surgical indication(early indication: valvular dysfunction or HF or 1cm mass) then consider CT surgery consult.
- device infection: remove it. continue Abx for 7-14days after removal. 72hours of negative culture for reimplant.
- LVAD: IV -> PO(chronic suppression)
- Medical management
- empirical antibiotics: Vancomycin.(trough 15-20). (if unstable, then add Cefepime)
- antithrombotics: no benefit unless there is other indication.
But if there is MS with Afib, then start AC.
But if there is ICH/Ischemic stroke likely 2/2 septic emboli, then stop AC/ASA.
antithrombotics: held ASA d/t increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
- taylored antibiotics (per ID, prosthetic valve has different combination regimen for SA or enterococcus).
- prophylaxis: Ix(h/o IE, congenital heart disease + a(residual), MV ring, prosthetic valve, OHT with h/o valvulopathy)
+ respiratory procedure with biopsy/incision or dental procedure. (mainly)
- method: amoxicilin 2g (30mins prior) or clindamycin 600mg or azithromycin 500mg. (iv cefazolin as well).
- Unusual bacteria: False-positive culture results occasionally occur. Organisms for which it can be difficult to distinguish between pathogenicity and contamination include Cutibacterium (formerly Propionibacterium) acnes,
Gram positive rods: Corynebacterium species, Bacillus species,
Coagulase-negative staphylococci. => repeat culture and start VANCOMYCIN ?
- Culture negative IE(7days negative): empirical combination therapy such as Vancomycin+Cefepime(Acute) or Vancomycin+Augmentin(subacute) or Vancomycin + Ceftriaxone etc. BUT mainly consult ID at this point for sure.

# Empirical antibiotics and target coverage
(https://viewer.microguide.global/secure/8b046be8-fccc-43e6-93f7-10b4928a7548)
Ds-Empirical Abx.-Coverage.
# Sepsis / Septic shock
- SIRS criteria: HR>90, RR>20, WBC>12 or <4 or>10% band, Fever >100.4
+ BP criteria(from qSOFA: AMS, RR>22, sBP<100)
Septic shock: Sepsis + sBP<90 or MAP<70; require pressors(NE, Vasopressin, and EPI)
- Lactate(>4; severe sepsis: UOP <0.5cc/kg/hr; ALI; AKI(Cr>2); AMS; Bil>2; Pls<100K; etc.)
- Basic labs: CBC, CMP, PT/PTT, Troponin
- Infection workup: Blood culture X2(one pph, one from vascular access device unless within 48hours - no risk)
UA/Urine Culture; Sputum/respiratory culture; wound culture; stool workup = per clinical scenario.
- CXR
Possible CT abd/pelvis(abdominal workup)
- Sources control(m/i): identification and appropriate antibiotics(key)
- REMOVE vascular access if it's suspected. (however can wait if it's not clear at this point clinically) cf. PICC part
- IVF
- empirical antibiotics: per suspected source(SA, Str = can be anywhere. less likely in GI, GU though but possible.)
* HAP/UNKNOWN >>> ABD >>> BLOOD STREAM >>> UTI
1. UTI: CEFEpime(or ZOSYN) (Pc. allergy: Levofloxacin and Gentamicin=nephrotoxic) = only G(-) coverage
2. central line: VANC and CEFEpime(or ZOSYN).= MRSA, G(+) and G(-) Coverage
3. abdominal: VANC and ZOSYN. (Pc allergy: VANC and Cipro and Metronidazole and Gentamicin=nephrotoxic) =
MRSA, G(+) and G(-) both coverage why? enterococcus faecium(is not covered by ZOSYN, covered by VANC!, surely
covered by levaquin)
- @ ICU: VANC and ZOSYN and Gentamicin (or micafungin 100mg iv q24hr)
- diverticulitis: ZOSYN will be good enough. = cover G(-) and Anaerobe coverage.
4. HAP~HCAP(3mo.): VANC and ZOSYN and LEVAQ
- CAP:
5- unknown:VANC and ZOSYN and LEVAQ
* In my approach: Pc allergy => Try meropenem.
* LEVAQ: super coverage even including G(+; MRSA), G(-; Pseudomonas), atypicals
# Empirical antibiotics coverage(Type, disease, target)
# Blood stream infection(CLABSI/endocarditis):
- CLABSI: VANC+CEFEPime.
- Endocarditis: VANC(cover more than 80% of bacterias which are G(+) in endocarditis). cf) HACEK, G(-) is possible for
+ CEFEpime(in unstable patient, such as sepsis!!)
# Skin/Soft/Bone: purulent or non purulent and/or systemic involvement !!
- Non purulent cellulitis: VANC+ZOSYN(severe= double coverage even broader stronger! )
(cellulitis, erysipelas; more superficial, superficial lymphatics involvement=milder disease upto moderate..)
Cefazolin IV(moderate, mild)
- purulent cellulitis with (abscess or drainage): VANC(Severe)
Bactrim DS or Doxycycline or Clindamycin (Moderate=systemic sign)
No abx(abscess <5cm & no systemic symptom)
- Necrotizing: VANC+ZOSYN+Clindamycin(double coverage and strong cover for strep.)
- osteomyelitis
# Respiratory
-bronchitis
-pneumonia
- CAP
- HCAP
- HAP
# GI
- enterocolitis
- ischemic colitis
- diverticulitis
- hepatic abscess?
# GU(UTI); symptom= dysuria, frequency, suprapubic pain, urgency, and hematuria
generalized symptom= fever, chills, rigors, fatigue, malaise = need to check.
- cystitis
- pyelonephritis: n/v ..
APN= flank pain, costovertebral angle tenderness, and nausea/vomiting
# CNS
- meningitis
- encephalitis
# Myocarditis - mimicking like CAD(Takotsubo), ADHF, or Arrhythmia.
- R/O ACS: serial troponin and EKG
- Acute(<3mo.) vs Chronic(>3mo.)
- Clinical suspected (sx=CP, SOB, Fatigue, palpitation, syncope, cardiogenic shock)
Diagnostic criteria (EKG: 1-3AV block, BBB, ST, Q, TWI, afib, VT; Troponin; Echo =regional/diffuse dysf.)
AND no other cause(such as CAD>50%, Valvular disease, CHD, hyperthyoridism, sarcoidosis)
= 1 clinical + 1 diagnostic = 2 diagnostic
Other supportive symptom = fever(in 1mo.), toxic agent, and autoimmune disease.
- Labs: CBC, CMP, PT/PTT, Troponin I, BNP, ESR, hsCRP(vs. CRP), TSH(hyperthyroidism can mimic)
- CXR, TTE(R/O Takotsubo) and/or CMR (+-CAG)
- Avoid NSAIDS(including ASA), Exercise(abstain from for 6 mo. and reeval), and EtOH.
- Manage ADHF, Arrhythmia as usual
- Fulminant myocarditis(shock status):
high dose steroids(high dose = more than 30mg prednisone a day; cf. less than 7.5 = low)
(reference. AHA scientific statement from Dr. Kociol et al.)
- 1g methyl prednisolone for 3 days and Prednisone 60mg with 10-mg/kg taper. (with 5-7.5mg maintenance)
- if hypotensive, consider NE than dopamine (esp. AMI shock, NE is preferred) or mechanical support.
- CAG +- EMB
[ ] how to r/o or r/i with pericarditis with myocarditis
# myopericarditis: treat as myocarditis but Colchicine can be useful for pericarditis. (But avoid ASA nor NSAIDS.)
# Acute pericarditis: Colchicine or NSAIDs(including ASA)
# Chronic pericarditis
# Recurrent pericarditis